- In a real building, you would need windows in every storey. So
for each storey of your model, half the length of the outside perimeter
(including the width of the pillars) must be left completely clear
of any materials between the top of one floor and the bottom of
the floor above.
Refer to Figures A and B for calculation details.
|
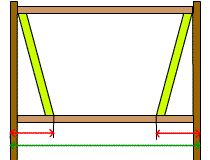
- Figure A shows the side view of an example model. The green arrow shows the length between the outmost columns (including the width of the columns), and the red arrows show the lengths that are taken up by the bracings.
|
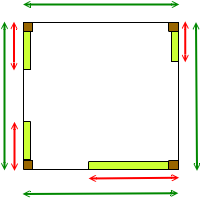
- Figure B shows the plan view of the same model as in Figure A. The perimeter, L, of the model is calculated by adding up the lengths of the green arrows. The total length occupied by materials, x, is equal to the summation of the lengths marked by red arrows. The following equation must be satisfied for this rule :
|
x / L
<= 1 / 2
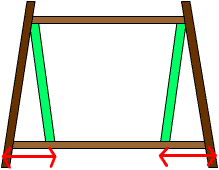
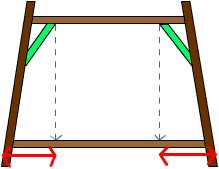
The length x is counted as the projection length on the bottom beam for models with different story width. (As shown in Figure C¡BD)
|
| |
|
Figure A (elevation) |
Figure B (plan) |
| |
|
| |
|
|
|
Figure C (elevation) |
Figure D (elevation) |
|
|